Oil Immersed Transformer vs Dry Type Transformer
Differences between oil immersed transformer and dry type transformer
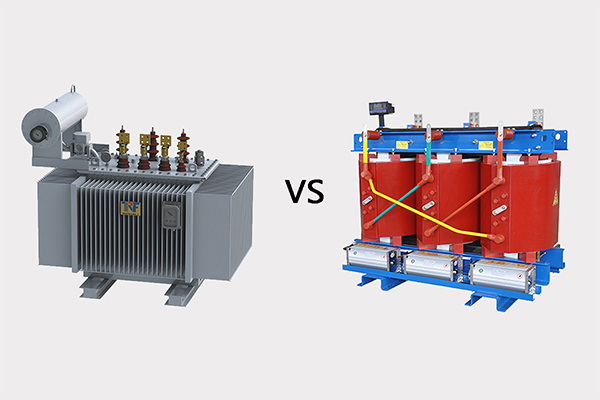
1. Price comparison - dry transformation is more expensive than oil.
2. Capacity comparison - the capacity of oil transformer is generally larger than that of dry transformer. Dry type transformers are generally suitable for power distribution. Most of them have a capacity of less than 1600KVA and a voltage of less than 10kV, and some of them have a voltage level of 35kV; The oil transformer can achieve all capacity from small to large, and the voltage level can also achieve all voltages.
3. Comparison of places of use - dry transformer is generally used in comprehensive buildings (basement, middle floor, roof, etc.) and densely populated places. The oil transformer is used in an independent substation. The transformer in the box transformer generally adopts dry transformer, and the outdoor temporary power generally adopts oil transformer.
4. Volume comparison - the volume of oil transformer is larger than that of dry transformer. Therefore, when using oil transformer, the space is required to be spacious. When the space is crowded, only dry transformer can be used.
5. Comparison of environmental requirements - generally speaking, the heat dissipation effect of oil transformer is better than that of dry transformer. Dry type transformers are generally insulated with resin, which is cooled by natural air and large capacity is cooled by fan. Oil type transformers are insulated by insulating oil, and the heat generated by the coil is transferred to the radiator (fin) of the transformer by the circulation of insulating oil inside the transformer.
6. Appearance comparison - different packaging forms, dry-type transformer can directly see the iron core and coil, while oil transformer can only see the shell of the transformer.
7. Comparison of lead forms - most dry-type transformers use silicone rubber bushing, while most oil transformers use porcelain bushing.
8. Comparison of load bearing capacity - generally, dry-type transformer should operate under rated capacity, while oil transformer has better overload capacity.
In general, the fundamental reason for the difference between the two is that the cooling medium is different. The oil change is based on transformer oil (of course, there are other oils such as β Oil) is used as cooling and insulating medium, while air or other gases such as SF6 are used as cooling medium for dry transformer. Oil transformer is to place the body composed of iron core and winding in an oil tank filled with transformer oil. The dry transformer often encapsulates the iron core and winding with epoxy resin. There is also a kind of non encapsulated type which is widely used now. The winding is impregnated with special insulating paper and special insulating paint to prevent the winding or iron core from moisture.
Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The oil transformer has low cost and convenient maintenance, but it is combustible and explosive. Due to its good fire resistance, the dry transformer can be disassembled for transportation and convenience, clean and easy to maintain. It does not need a base and has no oil seepage pool. It can be installed in the load center area to reduce voltage loss and power loss. However, the dry transformation has the advantages of high price, large volume, poor moisture and dust resistance, and high noise.
Due to the need of fire prevention, oil immersed transformers are generally installed indoors or outdoors, while dry-type transformers must be installed indoors. Generally, they are installed in the low-voltage distribution room side by side with the low-voltage distribution cabinet.