A traditional distribution automation under coordination by recloser plus sectionalizer
Recloser and Sectionalizer Coordination
--Achieving Distribution Line Automation under Traditional Condition --
-- Realizing Distribution Automation without SCADA System --

Key words: #recloser #sectionalizer #distribution automation #Semi Smartgrid
Summary: {%seoKeyword#6%}
Under the condition of no communication network, how to realize the intelligent distribution?
When the distribution line breaks down, how to make quick judgment, intelligently remove the fault section, ensure the normal operation of the non fault section, and reduce the power cut range?
The recloser and sectionalizer work together to realize the semi intelligence of the traditional power grid and automatically and effectively isolate more than 95% of the fault sections.
-----------------------------------------------------------
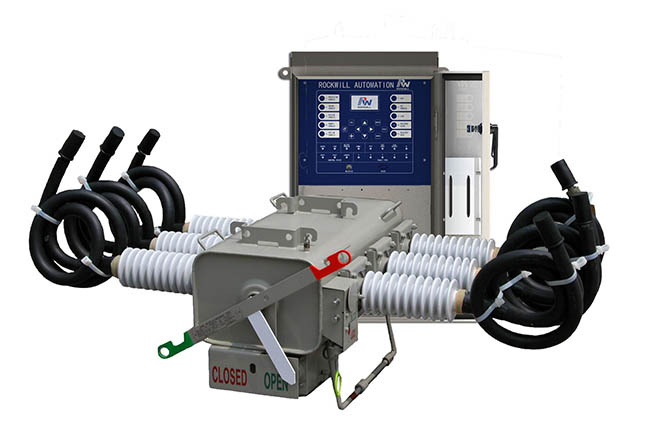
Recloser is a kind of intelligent switchgear used in distribution automation, which has control and protection functions. It can detect the fault current and automatically open and close the AC line according to the predetermined opening and reclosing sequence, and then reset and lock automatically. The recloser can be opened and closed for many times according to the preset action sequence, generally there are four times of fast and slow combination of opening and closing. The recloser has two kinds of protection: timing limit and inverse time limit.
There are two types of recloser: current time type and voltage time type. It is called current time type that reflects the reclosing of fault current after tripping. This recloser can be used for protection trip and realize 1-3 recloses. Voltage time recloser is the line voltage loss opening, delay reclosing after incoming. Voltage time recloser is often used in loop network as contact recloser.
Sectionalizer is an automatic switching device used to isolate the fault line section in the distribution network. It generally cooperates with the recloser or circuit breaker or fuse, and is connected in series with the load side of the recloser and circuit breaker, and automatically opens when there is no voltage or current. According to the different principle of fault identification, the sectionalizer can be divided into two types: "overcurrent pulse counting type" (current time type) and "voltage time type". The current time sectionalizer is usually used in combination with the previous stage switchgear (recloser or circuit breaker). It can't cut off the short circuit current, but it has the ability of "memorizing" the action times of breaking the fault current of the previous stage switchgear. Voltage time reclosing sectionalizer controls its action by the time of pressurization or voltage loss. After voltage loss, it opens, closes or locks after pressurization.
Application of recloser and sectionalizer in radiation network
According to the user's load, different structures of distribution lines have different combinations. Figure 1 shows the operation process of current time recloser and overcurrent pulse counting sectionalizer in case of line fault.

Figure 1 Application of recloser and sectionalizer in radiation network
In Figure 1, the short-circuit current at the outlet of substation is 1400A, SJ = 100mva, UJ = 10.5kv, L1 section conductor is lgj-95, the line length is 4km, the total reactance unit value of transformer is 0.91 × 10-3; L2 section conductor is lgj-70, the line length is 2km, the total reactance unit value of transformer is 0.735 × 10-3; L5 section conductor is lgj-50, the line length is 3.5km, and the total reactance unit value of transformer is 0.16 × 10-3. According to the above parameters, the maximum and minimum short-circuit current values of each point of the line and the rated current of each branch line are obtained. The maximum terminal short-circuit current of L5 section is 819a and the minimum is 709a; the maximum terminal short-circuit current of L2 section is 1068a and the minimum is 925a. The rated current at the outlet of substation is 307.2a, the rated current at the outlet of L2 section is 50a, and the rated current at the outlet of L5 section is 108.6a.
The t-i characteristic curve of the two reclosers selected in the figure is shown in Figure 2. The vertical coordinate of the a curve represents the maximum value of the actual action time, while the slow characteristic curve is drawn according to the average value of the fault current passing time as the vertical coordinate. The general error is not more than ± 10%. The horizontal coordinate is the multiple of the minimum tripping setting current. The starting point of the curve corresponds to the minimum action current value and action time. Rvb1 is the recloser in the substation, and rcw1 is the outdoor recloser, both of which are current time type. Rvb1 is set as one fast and three slow (1a3c), and the starting current is set as 400A. Rcw1 is set as two fast and two slow (2a2b), and the starting current is set as 200A. The starting current value of the recloser is generally set at 1.3-1.6 times of the rated current, and the starting current must avoid the inrush current. The reclosing interval is 2S. Rps1, rps3, RPS4, RPS5 are counting times

Fig. 2 t-i characteristic curve of recloser
It is a 2-time 4-segmenter and rps2 is a 3-funded segmenter.
In case of short circuit fault at D1, the minimum short circuit current is 709a, reaching the starting current value of recloser. If it is a transient fault, as shown in Figure 2, the recloser rvb1 at the substation outlet and the line recloser rcw1 operate once according to the fast curve (curve a). (the starting current of recloser rvb1 and rcw1 is different, the operation time of recloser rvb1 is 0.07s, and the operation time of recloser rcw1 is 0.05s, but the operation time of rvb1 and rcw1 are milliseconds, so it is difficult to distinguish the operation sequence in the operation time Therefore, the action sequence of recloser can only be distinguished according to the speed curve. The sectionalizers rps2 and RPS4 are still in the closed state due to not reaching the set count times, and reclose after 2S, so as to restore the line power supply. If it is a permanent fault, the line recloser rcw1 will act according to the fast curve again. The recloser rvb1 in the substation will not act due to the slow curve (C curve) set, and the sectionalizer RPS4 will reach the set counting times of opening and dropping, isolate the fault section, and the line recloser rcw1 will reclose after 2S, so as to restore the power supply of other sections of the line.
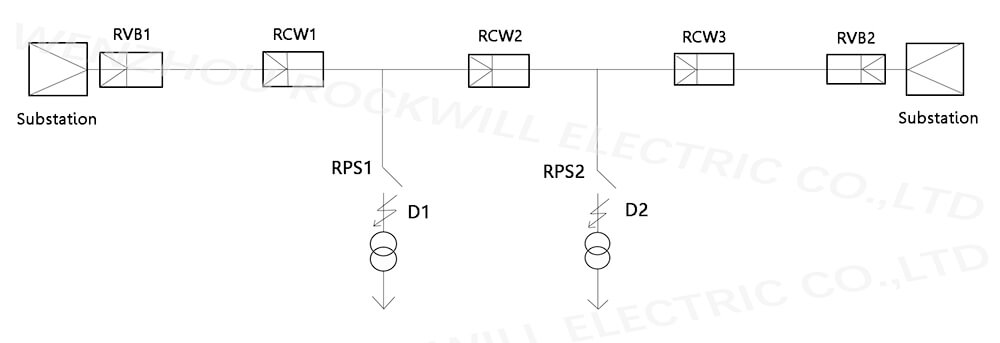
Fig. 3 application of recloser and sectionalizer in ring network
In case of short circuit fault at D2, the minimum value of short circuit current is 925a, reaching the starting current value of recloser. If it is a transient fault, as shown in Figure 2, the recloser rvb1 at the outlet of the substation acts once according to the fast curve, the number of times that the sectionalizer RPS5 fails to reach the setting is still in the closing state, the recloser rvb1 recloses after 2S, and the line power supply is restored. If it is a permanent fault, the recloser at the outlet of the substation trips again according to the slow curve (C curve), the sectionalizer RPS5 reaches the set count times of opening and dropping, isolating the fault section, and the recloser recloses and restores the power supply of other lines after 2S. The purpose of setting the first action of the recloser at the outlet of the substation as a fast curve is to eliminate the instantaneous fault and protect the line equipment.
Application of recloser and sectionalizer in loop network
With the rapid development of distribution automation and power market, ring network structure has become the main trend in recent years. Taking Figure 3 as an example, when the contact recloser is not connected in normal operation, the main lines of the two substations establish a standby contact relationship with each other. The ring network structure in Figure 3 is applicable to areas where only a simple communication system is established in the transformation of distribution network automation and there is not much capital investment. In the areas where the communication system is relatively developed, it is suggested to use the ring network structure with background control. The automation and communication level of the ring network structure with background control are relatively high. The distribution system automation has been realized in Japan and other developed countries in the 1990s.
As shown in Figure 3, a and B are two substations. Normally, rvb1, rcw1, rcw3, rvb2, rps1, rps2 are closed. Rvb1 and rvb2 reclosers are current time type indoor reclosers, which are set as one fast and three slow (1a3c), and the reclosing interval is 2S. Rcw1, rcw2 and rcw3 are voltage time type outdoor reclosers. The delay time of closing of rcw1 and rcw3 is 3S, and the two times of closing are not locked successfully. Rcw2 is the contact recloser. Under normal conditions, the line is in the opening state, which is set as one-time closing unsuccessful locking. Rps1 is the segmenter with 2 counts, rps2 is the segmenter with 1 count.
In case of fault at D1, the outlet recloser rvb1 performs fast curve action once, the reclosers rcw1 and rcw2 detect the line voltage loss, rcw1 opens, the sectionalizer rps2 reaches the set count times of opening and dropping, the recloser rvb1 recloses after 2S, the recloser rcw1 delays reclosing for 3S, and the power supply of other parts of the line is restored. In case of D2 fault, if it is transient fault, rvb1 of outlet recloser performs fast curve action once, rcw1 and rcw2 of recloser detect line voltage loss, rcw1 opens, Rps1 of sectionalizer fails to reach the set count times and is still in the closing state. If it is a permanent fault, the outlet recloser rvb1 will open again, the recloser rcw1 will detect the line voltage loss and open again, and the sectionalizer rps1 will reach the set count times to open and close the fault section. After the recloser is closed successfully, the power supply of other lines will be restored.
In case of permanent failure at D3, recloser rvb1 will be opened and finally locked. The recloser rcw1 is then changed from the original state to one-time closing without successful locking. The recloser rcw2 is closed within a slightly longer time limit than rcw1, the L1 line is reversely powered by substation B, and the recloser rcw1 is opened and locked due to closing at the fault point. Section L2 and branch lines are powered by substation B.
In case of permanent fault at D4, the outlet recloser rvb1 performs fast curve opening, the reclosers rcw1 and rcw2 detect the line voltage loss, the rcw1 opens, the recloser rvb1 recloses after 2S, the recloser rcw1 delays for 3S to close at the fault point, and the final opening is locked. Rcw2 of the contact recloser is closed in time delay, and the final opening locking is not eliminated due to the fault.
Conclusion
The recloser has a long history of use and perfect functions. Because of its high success rate of reclosing, less comprehensive investment, and the advantages of cooperation with the sectionalizer, such as eliminating instantaneous faults, minimizing the scope of power failure, less maintenance work, and safe and reliable equipment, it has great use value in distribution automation.
Learn more information about Rockwill>>> {%seoKeyword#14%}
Technical Service:
ROCKWILL®, China. Provide with best support
Tel: 0086-577-27869969
Email: barry@rockwill.cn